- Prepare for Back to School - Propel growth and light the path towards a brighter future.
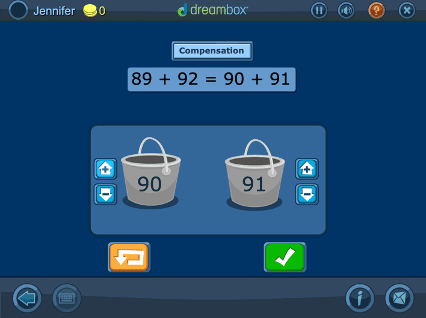
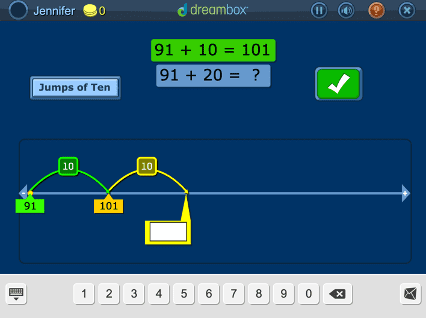
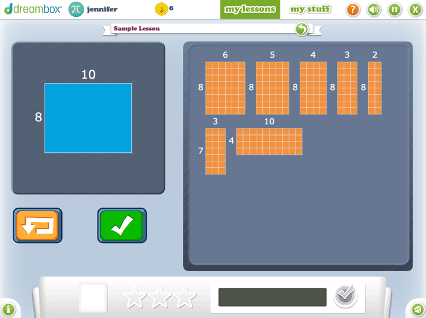
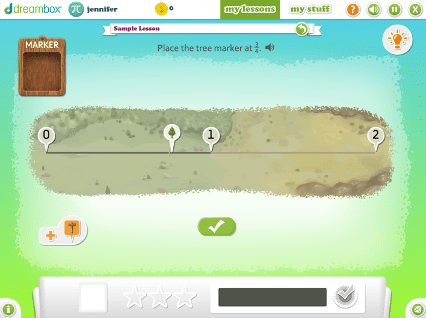
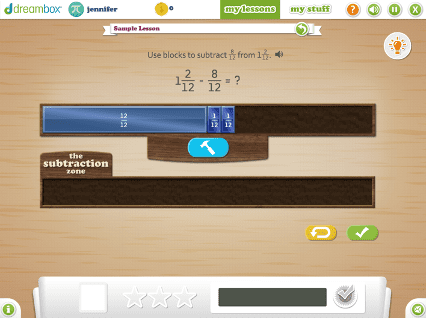
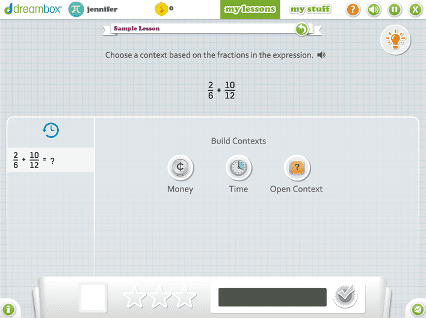
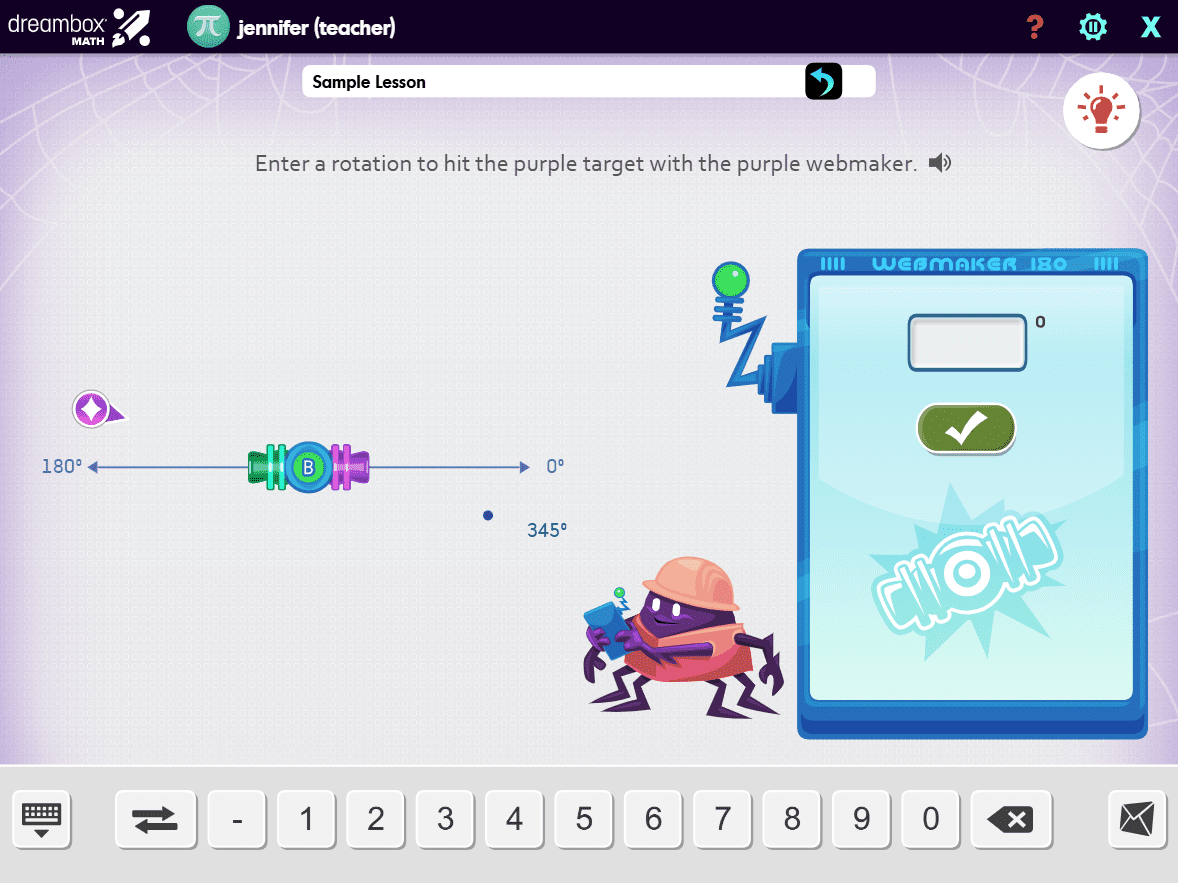
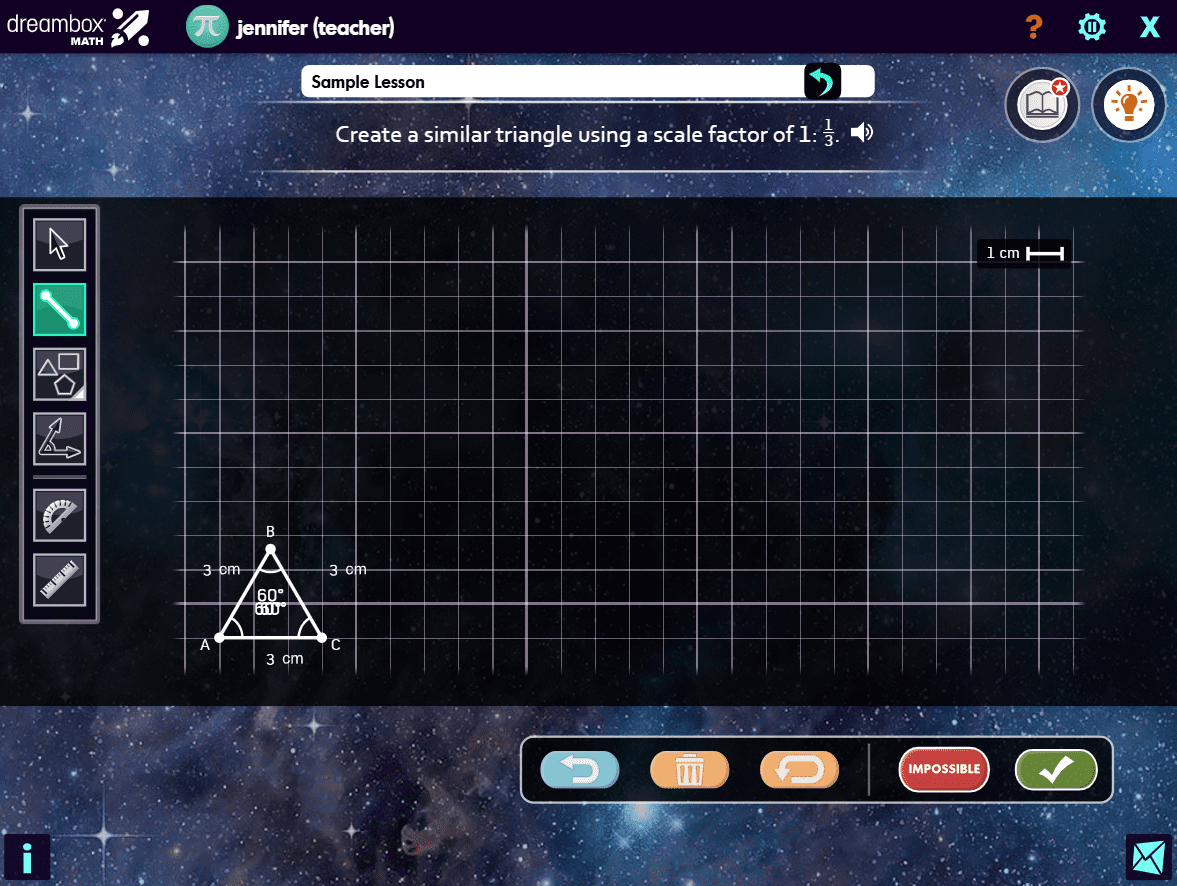
DreamBox offers over 2,000 lessons with millions of paths through the curriculum. To engage students exactly where they are, it adjusts in real-time, adapting hints, level of difficulty, pace, and sequence.